
Android is belatedly getting a Bluetooth tracker feature which doesn't rely on proprietary apps. Long-time readers will know that back in 2016 I reviewed both the Chipolo and the TinTag. Both of those were adequate at finding things which were in range of your phone, but hopeless at finding lost items - because they required everyone to have a special app installed. But now, under pressure from …
Continue reading →

Here's a "fun" thought experiment. Imagine a website which let you sign in using only your username and TOTP code. No passwords. No magic links emailed to you. No FIDO tokens. No codes via SMS. Just a TOTP generated and displayed on your device. Is that useful? Sensible? Practical? It's certainly technically possible. Store the username, store the TOTP seed, done. Your users can now log in. …
Continue reading →

A decade ago, I appeared on the 361 Podcast to give my advice about mobile security. This was the era of the iPhone 5 and Android KitKat. BlackBerry was trying to have (yet another) resurgence and Nokia was desperately trying to keep Windows Phone alive. What advice did I give then, and is it still relevant? Stay Sceptical In at number five is just stay sceptical. I mean, quite often, lots…
Continue reading →

For lots of online accounts, a date of birth is nothing more than a very weak second factor. The majority of places aren't checking your identity, cross-referencing your birthdate, and personalising your experience based on your Zodiac sign. At most, they'll wish you a happy birthday and / or let you recover your account by providing your date of birth. But, of course, lots of people know your…
Continue reading →

Yeah. Yeah, I reckon so. Under the right circumstances. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA, 2FA, TOTP, whatever you want to call it) is pretty nifty. You scan a QR code and your phone will continually generate a set of one-time passwords which are synchronised with a remote server. There's nothing stopping multiple people from scanning that QR code! They will each have the same password displayed …
Continue reading →

I've been writing about QR codes since 2007 - long before they were fashionable. Because QR Codes are so cheap to produce, there has always been a concern that attackers might print out their own codes and stick them over legitimate ones. When I first wrote about QR Hijacking in 2011, I said that such attacks were usually easy to spot: Recently, a new wave of QR Hijacking attacks have been…
Continue reading →

Shakespeare, famously, shunned computers. Like some sort of retro hipster, he didn't write his plays on a laptop, refused to use spellcheck, and didn't register his copyright on the blockchain. Lord, what fools these mortals be! What would Shakespeare's plays have been like if their characters understood basic cybersecurity? Now, it is true that very few of his plays feature computers, but…
Continue reading →
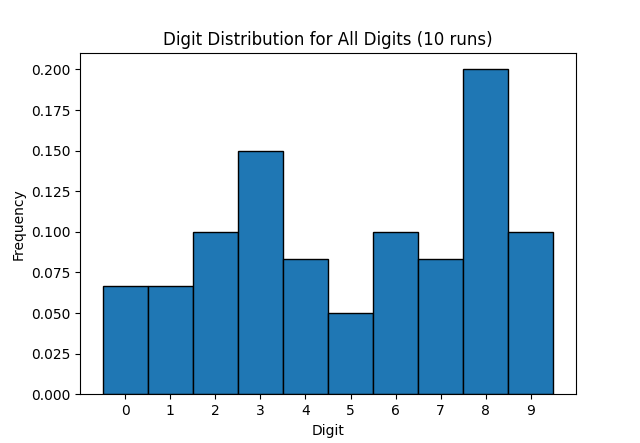
I'm pretty sure that the 2FA codes generated by my bank's TOTP app have a bias towards the number 8 - because eight is an auspicious number. But is that just my stupid meaty brain noticing patterns where none exist? The TOTP algorithm uses HMAC, which in turn uses SHA-1. My aforementioned brain is not clever enough to understand how that works. Although bigger, meatier brains have assured me it …
Continue reading →

Recently, WordPress got in contact with me to say they suspect that my password was exposed in some sort of data breach. Well, it's a day ending with a "y" - so of course some scumbag has pilfered my digital identity. WordPress mandated that I change my password. But was that really necessary? Firstly, the password was uniquely generated by my password manager. It isn't re-used anywhere else.…
Continue reading →
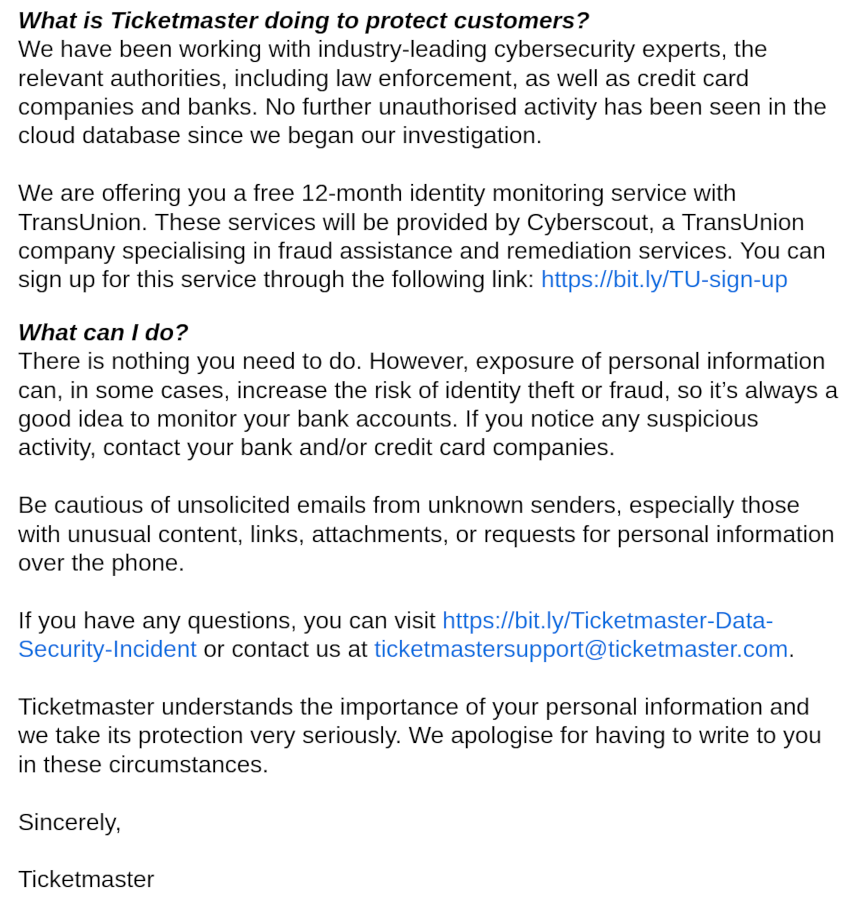
TicketMaster has joined the long list of companies to lose their customers' information. As is common, they sent out an email to warn poor sods like me who might have had our details snaffled. Their email is particularly poor and contains a delightful example of how not to communicate issues like this. See if you can spot it: In the same breath as warning their customers to look out for…
Continue reading →

Over the last few weeks, I've had several people ask me about the recent hack on the NHS. A ransomware attack has meant that several hospitals have cancelled operations and there is now an urgent demand for blood donors. What does it say about the state of NHS IT that this attack has happened? Nothing. Because the NHS was not hacked. Instead, a company they use to perform blood tests was…
Continue reading →

Everyone loves Dark Mode. It is kinder on the eyes, less energy intensive, and looks hecking cool. *5 seconds later* We regret to inform you that Dark Mode causes security bugs. (With apologies to Ben Ward) OK, OK. This isn't a particularly severe security bug, but I found it interesting. The Matrix messaging app "Element" lets you sign in to your account on multiple devices. In order to…
Continue reading →










